One-Time Passwords (OTPs) are becoming a common way to secure online accounts, validate transactions, and improve cybersecurity in a world that is becoming more and more digital. OTP bots are now tools for managing, interacting with, and even taking advantage of OTP systems. The definition of OTP bot, their legal and illegal uses, and the wider ramifications for people and organizations will all be covered in detail in this article.
What Is an OTP?
Usually employed as an extra security measure, an OTP, or one-time password, is a randomly generated code that is sent to a user’s phone or email. These passwords are meant to be used just once and are time-sensitive, frequently expiring in a matter of minutes. They provide an extra degree of protection on top of usernames and passwords and are essential to two-factor authentication (2FA) systems.
How OTPs Work
- Generation: When a user initiates a secure action (e.g., login or transaction), an OTP is generated by the authentication server.
- Delivery: The code is sent to the user via SMS, email, or a dedicated app.
- Validation: The user inputs the OTP on the website or application, and the system verifies its validity.
OTPs are considered a cornerstone of cybersecurity, but their effectiveness can be compromised by sophisticated tools like OTP bots.
What Is an OTP Bot?
A software tool made specifically to communicate with OTP systems is called an OTP bot. Depending on its design and use, it could help users automate legal procedures or be used maliciously to intercept or obtain OTPs from unwary victims.
Types of OTP Bots
- Legitimate OTP Bots:
These are used by businesses to streamline operations, such as verifying users or automating repetitive tasks like OTP generation and validation in internal systems. - Malicious OTP Bots:
Cybercriminals use these bots to trick individuals into revealing OTPs, enabling unauthorized access to sensitive accounts or data. These bots often target financial institutions, e-commerce platforms, or any service employing OTP-based security.
How OTP Bots Work
Legitimate Use Cases
- Streamlining Internal Processes:
Large organizations utilize OTP bots to automate OTP-related processes, reducing human error and saving time. - Customer Support Automation:
Businesses integrate OTP bots into customer support workflows, ensuring faster assistance for OTP-related queries.
Malicious Use Cases
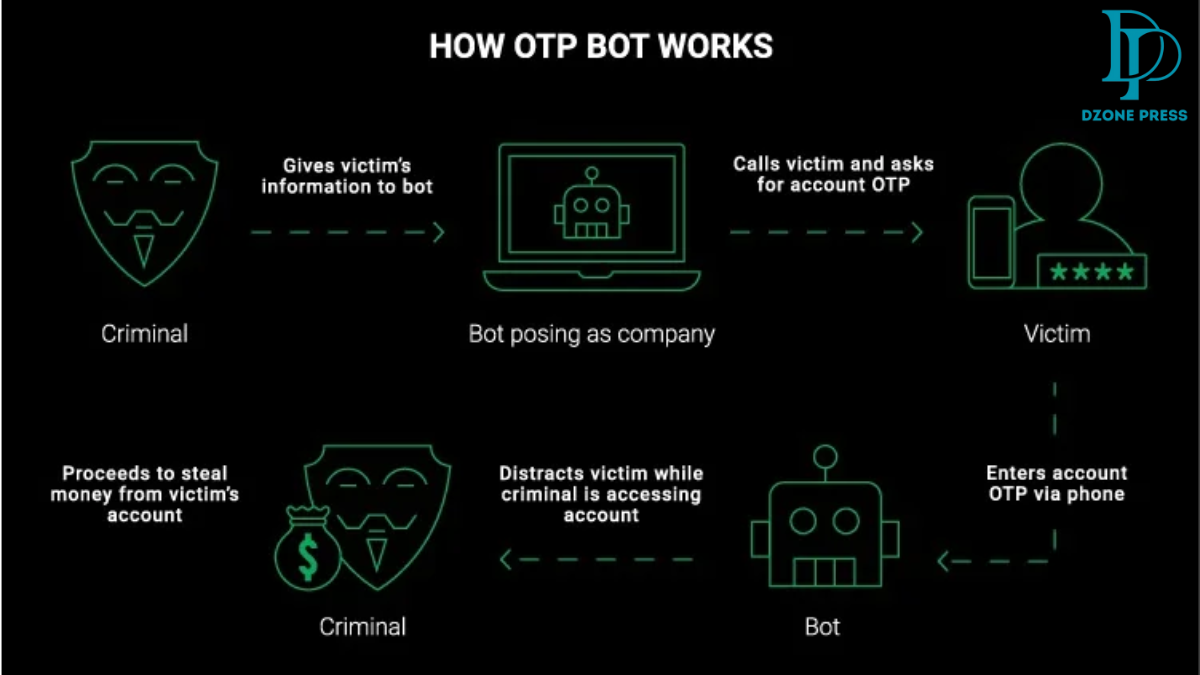
Malicious OTP bots are typically employed in phishing schemes or account takeovers. Here’s how they work:
- Initiation: The attacker uses the bot to contact the target, posing as a trusted entity (e.g., bank or retailer).
- Deception: The bot asks the victim for their OTP, often under the guise of confirming a transaction or securing their account.
- Extraction: Once the victim shares the OTP, the attacker uses it to gain unauthorized access.
These malevolent bots circumvent the protection that OTPs are meant to offer by using automation and psychological manipulation.
Applications of OTP Bots
Although the presence of OTP bots draws attention to weaknesses, they also have a variety of uses in both legal and illegal fields.
Legitimate Applications
Automated Customer Verification
Companies with a large customer base use OTP bots to automate the verification process. Such bots could be used, for example, by an online retailer to confirm the identity of customers prior to issuing refunds or returns.
Enhanced User Experience
Businesses can provide faster answers to consumer questions and increase customer satisfaction by automating OTP-related operations.
Integration with Security Systems
Organizations frequently integrate OTP bots with cutting-edge cybersecurity solutions to ensure smooth two-factor authentication for clients and staff.
Malicious Applications
Financial Fraud
OTP bots are used by cybercriminals to gain access to banking or payment services, frequently leading to purchases or transfers that are not permitted.
Social Engineering Campaigns
These bots are used to improve phishing attempts by imitating official communication channels, which makes them seem more credible.
Credential Stuffing
In order to get around two-factor authentication systems and gain control of accounts, attackers combine stolen login credentials with OTP bots.
Implications of OTP Bots
The rise of OTP bots poses significant challenges for individuals, organizations, and cybersecurity professionals.
For Individuals
Privacy Concerns
Malicious OTP bots often harvest personal information alongside OTPs, leading to identity theft or financial loss.
Increased Vulnerability
If they are not careful, even users who follow good password hygiene can become targets of OTP bot schemes.
For Organizations
Financial Losses
Businesses targeted by OTP bot attacks may suffer from financial theft, data breaches, or reputational damage.
Compliance Issues
Businesses that do not sufficiently protect consumer data may be subject to legal action under data protection laws such as the CCPA or GDPR.
For the Cybersecurity Industry
Need for Advanced Solutions
Cybersecurity experts must continually innovate to counteract the evolving capabilities of OTP bots.
Increased Demand for Awareness Campaigns
Raising public awareness about the risks associated with OTP bots has become a priority for many organizations.
How to Protect Against Malicious OTP Bots
To mitigate the risks posed by malicious OTP bots, individuals and organizations should adopt robust security measures.
For Individuals
- Be Skeptical of Unsolicited Requests:
Never share OTPs with anyone, even if the request seems legitimate. - Enable Advanced Authentication Methods:
Consider using biometrics or app-based authentication instead of SMS-based OTPs. - Educate Yourself:
Stay informed about the latest phishing tactics and OTP bot scams.
For Organizations
- Implement Multi-Layered Security:
Combine OTPs with additional security measures like device fingerprinting or geofencing. - Monitor for Anomalies:
Use AI-driven tools to detect unusual login patterns or bot activity. - Conduct Regular Training:
Educate employees and customers about the risks of OTP bot attacks and how to avoid them. - Invest in Anti-Bot Technologies:
Deploy solutions specifically designed to identify and block bot traffic.
The Ethical Debate Around OTP Bots
The dual nature of OTP bots raises ethical questions about their development and use.
Legitimate Use Cases
Even though OTP bots might increase security and efficiency, their potential for abuse frequently outweighs their advantages. Developers need to make sure their tools are used safely and morally.
Regulating Malicious Use
Fighting cybercrime, particularly the abuse of OTP bots, is a growing priority for governments and regulatory agencies. To reduce these risks, more legislation and international collaboration are required.
The Future of OTP Bots
The capabilities of OTP bots will expand in tandem with technological advancements. AI and automation advancements will probably lead to the evolution of both benign and malevolent applications.
Trends to Watch
- AI-Driven Bots:
Enhanced by machine learning, OTP bots may become even more sophisticated, requiring equally advanced countermeasures. - Increased Regulation:
Governments may impose stricter regulations on the development and use of OTP-related technologies. - Shift to Passwordless Security:
As organizations move toward passwordless authentication systems, the role of OTPs—and thus OTP bots—may diminish.
FAQs
Q: What is an OTP bot?
A: One kind of automated program intended to communicate with users and retrieve one-time passwords (OTPs) is called an OTP bot. These bots can be used maliciously by fraudsters to phish or get around authentication systems, or they can help consumers verify OTPs during safe transactions.
Q: How does an OTP bot work?
A: Automating the process of obtaining or intercepting OTPs is how OTP bots work. When used properly, they integrate with messaging apps or programs to expedite verification. Maliciously, they could send false prompts or imitate trustworthy services to fool users into sharing OTPs.
Q: Is using an OTP bot safe?
A: The context determines this. When utilized in secure settings, legitimate OTP bots improve user experience and verification effectiveness. However, utilizing or engaging with fraudulent or unverified OTP bots poses serious hazards, including identity theft and unauthorized access to private accounts.
Q: Can OTP bots bypass two-factor authentication (2FA)?
A: Yes, in some cases, malicious OTP bots are specifically designed to bypass 2FA systems. They exploit user trust through social engineering tactics or phishing campaigns, convincing users to share their OTPs or login credentials.
Q: How can I protect myself from malicious OTP bots?
A: To safeguard against malicious OTP bots:
- Never share OTPs with anyone, even if they appear to be from a legitimate service.
- Verify sources of OTP requests before responding.
- Use strong authentication systems, like app-based authenticators or biometrics.
- Be cautious about phishing attempts through emails, calls, or SMS.
Q: What are the legitimate uses of OTP bots?
A: Businesses often use legitimate OTP bots for:
- Automating customer OTP delivery during login or transactions.
- Streamlining multi-factor authentication processes.
- Enhancing user convenience in apps or services requiring frequent verifications.
Conclusion
In the current digital environment, OTP bots can be both a help and a hindrance. Although they can automate and simplify procedures, their abuse exposes serious flaws in cybersecurity architectures. People and organizations can defend themselves against the possible threats posed by OTP bots by being aware of the risks and putting strong safeguards in place.
Navigating the potential and problems these instruments bring requires creativity, awareness, and education. Users, companies, and cybersecurity experts all have a responsibility to make sure that OTP bots are used for good rather than bad.